Home / News / What Are the Major Differences Between Perforated TPU Foam Sheet and Perforated PU Foam Sheet?
In modern manufacturing industries—particularly those involved in automotive interiors, footwear production, sports equipment, and protective padding—the choice of foam materials plays a decisive role in achieving the desired balance between flexibility, comfort, and durability. Among these materials, perforated TPU foam sheet and perforated PU foam sheet are two popular options that often serve similar purposes but differ significantly in performance characteristics, processing behavior, and end-use suitability.
Understanding Perforated Foam Materials
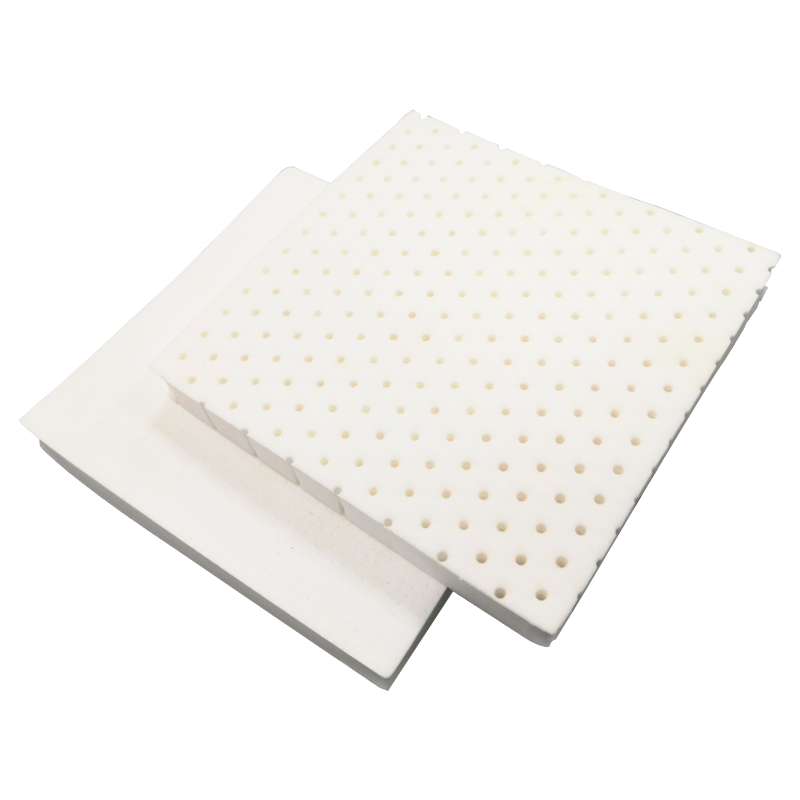
Before comparing the two materials, it is important to clarify what a perforated foam sheet represents. A perforated foam is a sheet material with a series of engineered holes or micro-perforations that allow air and moisture to pass through. This design enhances breathability, ventilation, and compression recovery, which are critical in performance-based and comfort-driven products.
Both perforated TPU foam sheet and perforated PU foam sheet share this perforation design but differ in their base polymer composition and cell structure, resulting in distinct physical and functional behaviors.
The Material Composition and Structure
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
A perforated TPU foam sheet is made from thermoplastic polyurethane, a polymer known for its high elasticity, abrasion resistance, and processability. TPU combines the flexibility of rubber with the strength and recyclability of thermoplastics. When expanded into a foam, it maintains excellent resilience while offering a soft tactile feel.
The cell structure of TPU foam tends to be more uniform and closed, meaning that when perforated, it allows controlled air permeability without compromising mechanical strength. This uniformity makes perforated TPU foam sheet particularly suitable for precision-engineered products requiring consistent cushioning and elasticity.
Polyurethane (PU)
By contrast, perforated PU foam sheet is derived from polyurethane, a material formed through the reaction of polyols and isocyanates. PU foam is typically available in flexible or rigid forms, but for perforated applications, the flexible type is most common. It features an open-cell structure that naturally allows airflow, and the addition of perforations further increases ventilation and softness.
While PU foam is lightweight and cost-effective, its chemical stability and mechanical endurance are generally lower than those of TPU foam, particularly under repeated stress or high-temperature environments.
Production and Processing Differences
The production processes for perforated TPU foam sheet and perforated PU foam sheet differ significantly due to their material characteristics.
Manufacturing of Perforated TPU Foam Sheet
TPU foam is typically created through extrusion or molding processes, where thermoplastic pellets are expanded under controlled conditions to form a lightweight, elastic foam structure. Once foamed, the sheet undergoes mechanical or laser perforation. The precision of perforation is important to maintain dimensional stability, especially in high-performance uses like automotive seats or footwear insoles.
Because TPU is thermoplastic, it can be reheated and reshaped, offering design flexibility. It can also be laminated with fabrics, mesh layers, or adhesive films, which expands its usage across multi-layer products.
Manufacturing of Perforated PU Foam Sheet
PU foam production, on the other hand, involves a chemical foaming reaction, typically through continuous or block foam formation. After curing, the foam is sliced into sheets, and perforations are added using mechanical punching. PU foam cannot be thermally remolded, so post-processing options are limited compared to TPU foam.
PU foam’s perforations are often coarser and less uniform, leading to greater airflow but less precision in structural control. This makes it ideal for applications prioritizing comfort and breathability rather than dimensional accuracy.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Comparison
The mechanical differences between perforated TPU foam sheet and perforated PU foam sheet form the foundation for material selection.
| Property | perforated TPU foam sheet | perforated PU foam sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic Recovery | Excellent – quickly regains shape after compression | Good – slower recovery under repeated compression |
| Abrasion Resistance | High – withstands wear and friction | Moderate – prone to surface wear |
| Tear Strength | Strong, retains integrity even with perforations | Weaker under tensile load |
| Density Range | Medium to high, offering firm support | Low to medium, providing softer cushioning |
| Air Permeability | Controlled, dependent on perforation pattern | Naturally higher due to open-cell structure |
| Thermoformability | Yes – can be molded and reshaped | No – thermoset material, not reshaped after curing |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable thermoplastic | Limited recyclability |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils and solvents | Moderate resistance |
From a performance perspective, perforated TPU foam sheet delivers greater structural stability and mechanical endurance, while perforated PU foam sheet offers superior softness and cost efficiency.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
When evaluating material longevity, durability, aging resistance, and environmental tolerance are crucial.
A perforated TPU foam sheet provides excellent resistance to hydrolysis, UV radiation, and temperature variations. It retains flexibility even under prolonged exposure to sunlight or moisture, which makes it ideal for outdoor equipment, automotive interiors, and industrial protective padding.
In contrast, perforated PU foam sheet tends to degrade more rapidly when subjected to UV light or humidity. Over time, it may exhibit yellowing, brittleness, or surface cracking. For applications with limited environmental exposure—such as indoor cushions or packaging inserts—PU foam remains a cost-effective solution. However, for extended performance life, TPU foam is the more reliable option.
Comfort and Breathability Performance
Both perforated foams are used to enhance comfort, airflow, and moisture management. Their performance in this area depends on the foam’s internal cell structure and perforation design.
A perforated TPU foam sheet maintains a balanced breathability. Its smaller, evenly distributed holes allow for controlled air exchange, ensuring that cushioning performance is not compromised by over-softness. The combination of elasticity and resilience helps maintain long-term comfort even under continuous load.
Meanwhile, a perforated PU foam sheet offers superior immediate softness and higher air permeability, especially beneficial in products like seat cushions, mattresses, and sound absorption panels. However, PU foam’s open-cell structure can absorb more moisture over time, potentially reducing durability if not adequately sealed or laminated.
In short, TPU foam balances comfort with durability, whereas PU foam prioritizes softness and ventilation.
Weight and Density Considerations
Weight is another factor influencing material choice. Perforated PU foam sheet is typically lighter, which can be advantageous for disposable or lightweight applications. Perforated TPU foam sheet, though slightly denser, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, ensuring longer lifespan and resistance to deformation.
Manufacturers must consider both density and compression load requirements when selecting the appropriate material. For instance, footwear midsoles and protective padding benefit from TPU foam’s supportive density, while comfort cushions and bedding components may perform better with PU foam’s lighter profile.
Thermal and Chemical Behavior
Thermal Resistance
Perforated TPU foam sheet maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range. It resists deformation at elevated temperatures and remains elastic at lower temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial uses. TPU foam’s melting point also allows heat bonding and lamination with fabrics or adhesives.
In contrast, perforated PU foam sheet may harden in cold environments and soften under heat, limiting its performance range. PU foam is best suited for controlled indoor conditions where temperature stability is consistent.
Chemical Resistance
In terms of chemical performance, TPU foam demonstrates excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and many industrial solvents. It is often used in environments requiring exposure to lubricants or cleaning agents. PU foam, while chemically resistant to some extent, is more prone to degradation when exposed to strong solvents or moisture for extended periods.
Processing and Fabrication Flexibility
From a manufacturing standpoint, perforated TPU foam sheet offers superior fabrication versatility. It can be:
- Thermoformed into complex shapes.
- Laser cut with precision without tearing.
- Bonded with textiles or films using heat or adhesives.
- Recycled and reprocessed for sustainable production.
Perforated PU foam sheet, on the other hand, cannot be reshaped once cured. Its perforations are typically added mechanically, and bonding requires adhesive lamination rather than thermal fusion. While PU foam is easier to punch and cut, it lacks the advanced formability and recyclability of TPU foam.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Cost remains one of the primary concerns for manufacturers and buyers. Perforated PU foam sheet is generally more economical due to its simpler production process and widespread availability. For products with shorter lifespans or non-critical performance requirements, PU foam is an ideal low-cost choice.
However, perforated TPU foam sheet justifies its higher price through enhanced performance, longer service life, and environmental advantages. In industries emphasizing sustainability, recyclability, and durability, the long-term cost efficiency of TPU foam often outweighs its initial investment.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability has become a critical factor in material selection. Perforated TPU foam sheet, being a thermoplastic, is fully recyclable. It can be reheated and remolded, reducing waste during production and enabling material recovery. Some manufacturers also use bio-based or recyclable TPU grades to align with eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Perforated PU foam sheet, being thermoset, cannot be remelted or reshaped after curing. Recycling options are limited to mechanical regrinding or chemical recycling, both of which are cost-intensive and less efficient. Therefore, in sustainability-driven industries, TPU foam has a distinct advantage.
Application Suitability by Industry
Both materials serve broad application ranges, but the choice depends on the desired performance outcome.
| Industry | Recommended Material | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Footwear & Insoles | Perforated TPU Foam Sheet | Breathable, elastic cushioning |
| Automotive Interiors | Perforated TPU Foam Sheet | Seat padding, headliners |
| Sports & Safety Gear | Perforated TPU Foam Sheet | Impact absorption, comfort lining |
| Furniture & Mattresses | Perforated PU Foam Sheet | Soft cushions, ventilation layers |
| Packaging & Display | Perforated PU Foam Sheet | Protective inserts, lightweight buffers |
| Medical Products | Perforated TPU Foam Sheet | Breathable supports, orthopedic pads |
This comparison shows that TPU foam dominates high-performance and long-life applications, while PU foam suits comfort-oriented, low-cost uses.
Market Trends and Buyer Insights
The global demand for perforated TPU foam sheet is steadily increasing, driven by consumer preference for comfort, breathability, and sustainability. Industries such as sportswear, automotive, and medical devices favor TPU foam due to its mechanical stability and recyclability.
Meanwhile, perforated PU foam sheet maintains a strong position in furniture, packaging, and bedding sectors, where cost and softness are primary considerations. Buyers are increasingly seeking hybrid solutions—such as layered composites of TPU and PU foams—to balance comfort and durability.
From a procurement perspective, buyers should consider the following when sourcing materials:
- Application environment (indoor vs. outdoor use).
- Load-bearing and compression requirements.
- Expected product lifespan.
- Budget and sustainability priorities.
Quality and Testing Standards
To ensure consistent performance, manufacturers of both foam types adhere to foam density, tensile strength, and compression recovery testing. For perforated TPU foam sheet, additional tests may include airflow resistance, dimensional accuracy, and thermal cycling durability. These quality checks confirm the foam’s suitability for precision applications.
Perforated PU foam sheet testing typically focuses on softness, comfort feel, and ventilation efficiency, making it more suitable for comfort-oriented evaluations.
Conclusion
While both perforated TPU foam sheet and perforated PU foam sheet share similar functions, their performance characteristics and industrial applications are notably different.
A perforated TPU foam sheet offers higher strength, durability, and recyclability, performing well in demanding environments such as automotive interiors, protective sports gear, and medical support components. Its thermoformability and chemical resistance further expand its application scope.
Conversely, perforated PU foam sheet remains a practical choice for cost-sensitive applications emphasizing softness, breathability, and comfort, such as furniture padding and bedding products.
Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on balancing performance expectations, lifecycle requirements, and budget. As industries continue to shift toward sustainable materials and precision engineering, perforated TPU foam sheet is expected to gain a stronger position in advanced product design and long-term industrial applications.


 English
English
 Español
Español
 ++86-0512-66079229
++86-0512-66079229