Home / News / What Makes Perforated TPU Foam So Durable and Long-Lasting?
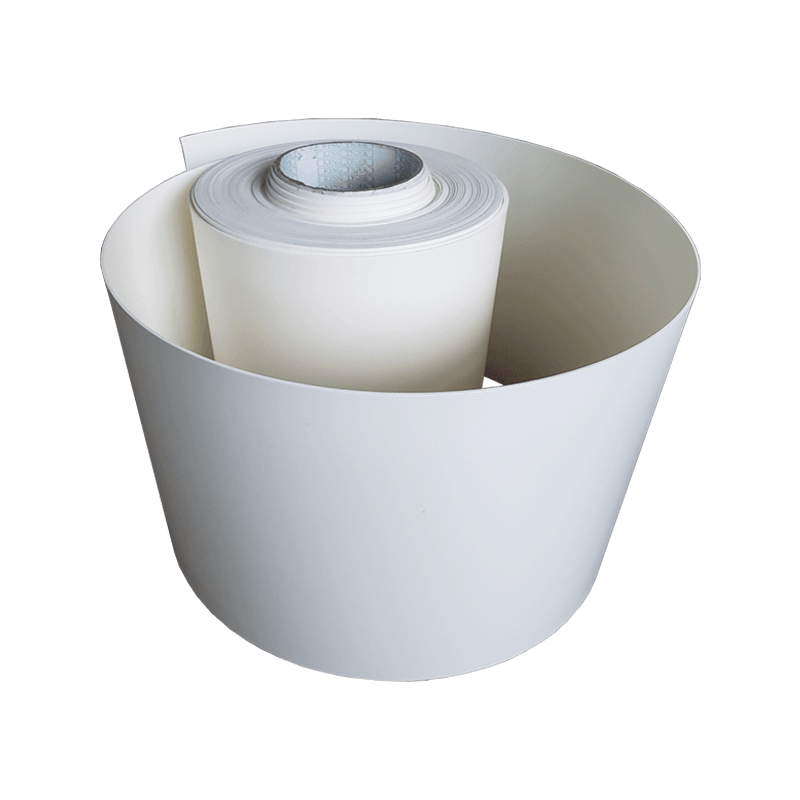
In the world of advanced polymer materials, few offer the unique combination of performance and resilience found in perforated tpu foam sheet. This material has become a cornerstone in industries where failure is not an option, from protecting sensitive medical devices to ensuring the safety of high-impact sports equipment. While its perforations are often celebrated for providing breathability and reducing weight, the true, often overlooked, value lies in its exceptional durability and longevity. For wholesalers, buyers, and engineers, understanding the intrinsic properties that contribute to this endurance is critical for selecting the right material for demanding applications.
The Foundational Chemistry of TPU: A Primer on Intrinsic Durability
To comprehend why a perforated tpu foam sheet is so durable, one must first understand the innate properties of its base material: Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU). TPU is an elastomer, meaning it exhibits both plastic and rubber-like properties. This unique behavior is not accidental; it is engineered at a molecular level. The polymer chains of TPU are structured in a block copolymer configuration, consisting of alternating hard segments and soft segments.
The hard segments provide structural integrity, creating physical cross-links that act as reinforcing points. These domains are responsible for the material’s high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and overall dimensional stability. They are the anchors within the molecular network. Conversely, the soft segments are responsible for the material’s elasticity, flexibility, and low-temperature performance. They allow the material to be stretched and compressed repeatedly, returning to its original shape with minimal permanent deformation.
This segmented structure is the primary reason for TPU’s renowned durability. When a force is applied, the hard segments distribute the stress throughout the material, preventing localized failure. The soft segments absorb the energy, allowing the material to flex and yield without cracking or tearing. This synergy creates a material that is exceptionally tough—resistant to wear, tearing, and impacts. Furthermore, TPU is inherently resistant to a wide range of environmental challenges, including ozone degradation, oxidation, and many oils, greases, and chemicals. This inherent chemical resistance prevents the material from breaking down or becoming brittle when exposed to harsh substances, a common point of failure for other elastomers. It is this robust chemical foundation upon which the long-lasting nature of perforated tpu foam sheet is built.
The Manufacturing Process: Creating a Coherent Cellular Structure
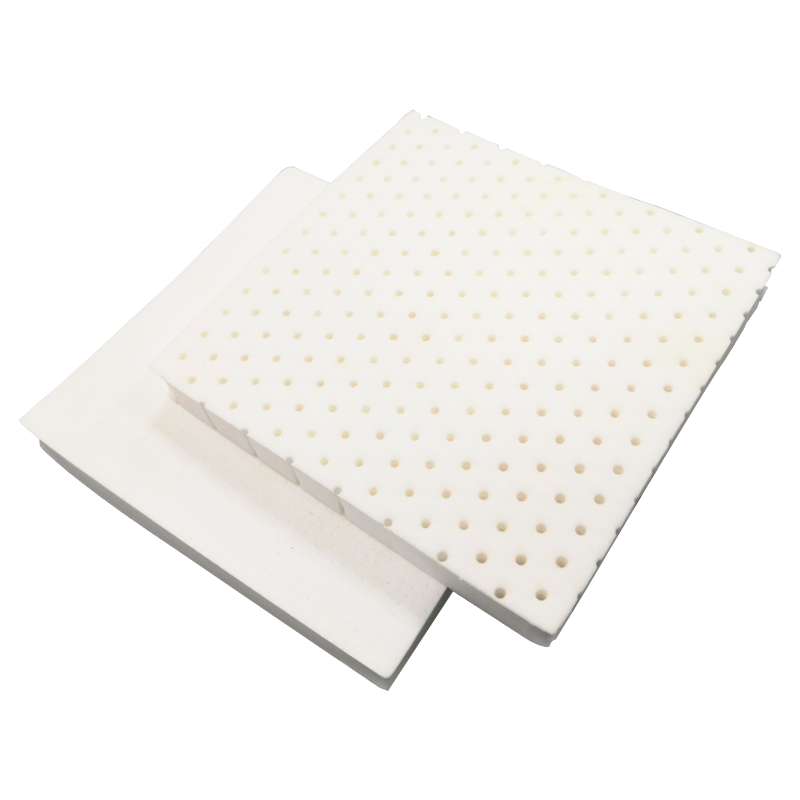
The transformation of solid TPU into a foam sheet is a critical process that directly impacts the final product’s durability. The foam is typically created through a chemical or physical foaming process, where a blowing agent generates gas bubbles within the molten TPU polymer. This creates a closed-cell structure, a matrix of tiny, individual gas-filled pockets trapped within the TPU walls.
A high-quality tpu foam sheet is characterized by a uniform and consistent cell structure. The size and distribution of these cells are meticulously controlled during manufacturing. A fine, consistent cell structure is paramount for durability. It ensures that stress and compressive forces are evenly distributed across the entire surface of the material. Larger or irregular cells can create weak points, areas where the material is more likely to collapse, crack, or fatigue under repeated loading. The foam’s density, measured in pounds per cubic foot or kilograms per cubic meter, is a direct reflection of this cell structure. A higher density often indicates thicker cell walls and a more robust matrix, contributing significantly to the foam’s load-bearing capacity and resistance to compression set.
The subsequent perforation process is not merely about creating holes; it is a precision operation that must complement the foam’s integrity. Perforations are typically added using specialized needles or dies that cleanly puncture the closed-cell foam. A high-quality perforation process ensures the holes are clean and precise without tearing or weakening the surrounding cell walls. This precision is vital. Poorly executed perforations can create micro-tears that act as initiation points for larger cracks under stress, severely compromising the material’s longevity. Therefore, a well-manufactured perforated tpu foam sheet benefits from both a coherent cellular structure and precise, non-destructive perforation, ensuring the final product retains the full strength of the base TPU material.
The Role of Perforations in Enhancing Functional Longevity
At first glance, adding holes to a material may seem counterintuitive to enhancing its durability. However, in the case of perforated tpu foam sheet, the strategic introduction of perforations contributes significantly to its functional longevity in several key ways. The most direct benefit is the management of moisture and air. In many applications, particularly in protective gear, medical supports, and outdoor equipment, the buildup of moisture from sweat or the environment can be detrimental. Trapped moisture can lead to the growth of mold and mildew, which can break down organic materials and cause unpleasant odors. It can also lead to the corrosion of adjacent components. By allowing air to circulate and moisture to evaporate rapidly, the perforations create a drier microclimate. This prevents the biological and chemical degradation associated with dampness, thereby preserving the material’s physical properties and extending its usable life.
Furthermore, perforations play a crucial role in mitigating heat buildup. When a foam material is compressed repeatedly, energy is dissipated as heat. In a closed-cell foam, this heat can become trapped, potentially leading to a breakdown of the polymer chains over time, a phenomenon known as thermal degradation. The perforations act as channels, allowing this generated heat to escape more efficiently. This passive thermal management keeps the material closer to ambient temperature during dynamic use, reducing thermal stress and helping to maintain the polymer’s mechanical properties. This is a critical factor in applications involving high-frequency compression and release, such as in insoles for footwear or vibration-damping pads.
Finally, the perforation pattern drastically reduces the material’s weight without a proportional sacrifice of strength. A lighter component experiences lower inertial forces during movement. In applications like athletic equipment or protective cases, this means the material itself, and the products it is part of, are subjected to less overall mechanical stress during use and transportation. Reducing overall stress directly correlates to a reduction in wear and fatigue, contributing to a longer service life for the end product. Thus, the perforations are not a compromise but an enhancement, adding a layer of functional durability that solid sheets cannot provide.
Key Performance Indicators: Measuring Resistance to Wear and Tear
The durability of any material must be quantified through standardized testing methods. For perforated tpu foam sheet, several key performance indicators are used to objectively measure its long-lasting properties, providing essential data for engineers and buyers.
One of the most important metrics is compression set resistance. This test measures a material’s ability to return to its original thickness after being subjected to a constant compressive load for a prolonged period at a specified temperature. A low compression set value is highly desirable, indicating that the foam will not permanently bottom out or lose its cushioning properties over time. The unique chemistry of TPU, with its strong physical cross-links, inherently provides excellent recovery. In a perforated foam, the structure allows the compressed air to be expelled and re-enter more freely, aiding in this recovery process. A material with a high compression set would quickly become thin and ineffective, whereas a high-quality perforated tpu foam sheet will maintain its thickness and performance characteristics for the lifespan of the product it is used in.
Abrasion resistance is another critical indicator, measuring the material’s ability to withstand surface wear from rubbing and friction. This is directly tied to the toughness of the TPU polymer’s hard segments. Standard tests involve rubbing the material against an abrasive surface under controlled pressure for a set number of cycles and measuring the weight loss or visible damage. The exceptional abrasion resistance of TPU means that the perforated sheets can maintain their surface integrity even when subjected to constant rubbing, such as inside a shoe against a sock or within a protective case against a device. This resistance ensures the perforations do not fray or tear and the surface does not become rough or patchy, preserving both function and aesthetics.
Tear strength measures the force required to propagate a tear once it has been initiated. The combination of the tough TPU matrix and the perforated pattern can influence this property. While a perforation is a designed feature, a high-quality sheet will demonstrate high tear strength, meaning any accidental cut or puncture will be difficult to spread, localizing the damage and preventing catastrophic failure. This is a vital safety and longevity feature in many applications. Finally, tensile strength and elongation at break describe how much force the material can withstand while being stretched and how far it can stretch before breaking. The high values typical of TPU indicate a robust and forgiving material that can absorb significant energy and deformation without failing, a hallmark of a durable product.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Foam Materials
To fully appreciate the durability of perforated tpu foam sheet, it is instructive to compare its properties with those of other common foam materials. Each material has its strengths, but TPU often stands apart in applications demanding maximum longevity.
A common alternative is cross-linked polyethylene (PE) foam, such as Volara or Minicel. PE foams are known for their excellent water resistance and good cushioning properties. However, they are polyolefins and can be more susceptible to creep and a higher compression set over time compared to TPU. They can also be more prone to tearing and may lack the same level of abrasion resistance. When perforated, PE foam can work well for packaging, but for dynamic, long-term load-bearing applications, it may not recover as effectively as TPU.
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is another widely used material, famous for its softness and ease of fabrication. It is a staple in the footwear industry for midsoles. However, standard EVA is known to compact over time, losing a significant portion of its cushioning due to its lower resilience and higher compression set. While advanced formulations can mitigate this, TPU foam generally offers superior resilience and durability. EVA can also be more susceptible to certain chemicals and can degrade when exposed to ozone, whereas TPU is highly resistant.
A comparison of key properties can be illustrated in the following table:
| Property | Perforated TPU Foam | Cross-linked PE Foam | EVA Foam | Impact on Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set | Very Low | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High | TPU retains shape & cushioning longest. |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair to Good | TPU surface wears slower, holes stay intact. |
| Tear Strength | High | Moderate | Moderate | TPU resists rip propagation more effectively. |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (oils, solvents) | Good | Poor to Fair | TPU withstands harsh environments better. |
| Flex Fatigue Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good | TPU withstands repeated bending without cracking. |
This comparison shows that while other foams are excellent for certain static or short-life applications, perforated tpu foam sheet provides a superior combination of properties that ensure performance is maintained over an extended period, even under demanding conditions of repeated stress and environmental exposure.
Applications Demonstrating Exceptional Service Life
The theoretical durability of perforated tpu foam sheet is proven in practical, real-world applications across diverse industries. In each case, the material’s long-lasting properties solve a critical design challenge.
In the field of medical and orthopedic devices, such as prosthetic liners, wheelchair seat cushions, and specialized supports, durability is directly linked to patient well-being and cost-effectiveness. These products are subjected to constant body weight, moisture, and cleaning with harsh disinfectants. The foam must not compress permanently, which would alter the fit and pressure distribution of a prosthetic, leading to discomfort and injury. It must resist degradation from sweat and repeated washing. The perforated tpu foam sheet excels here, providing consistent cushioning, breathability to maintain skin health, and the chemical resistance to withstand cleaning protocols, ensuring the device remains safe and functional for its intended lifespan.
The athletic and sporting goods industry is another area where the material’s endurance is paramount. Consider its use in high-performance insoles, midsole components, knee and elbow pads, or the padding inside a football helmet. These applications involve extreme, repetitive impacts, shear forces, and exposure to sweat. A material that breaks down, compacts, or loses its energy-return properties would not only degrade athletic performance but also increase the risk of injury. The foam’s ability to absorb impact after impact without permanent deformation, while managing moisture and heat, makes it a preferred choice for equipment where protection and performance cannot diminish over time.
For protective case liners used in the security, aerospace, and electronics sectors, the requirement is to protect sensitive and expensive equipment from shock and vibration throughout years of transportation and use. The foam liner must have an extremely low compression set to ensure it does not pack down after being compressed during shipping or storage. It must maintain a snug fit to prevent the device from moving within the case. The durability of the perforated tpu foam sheet ensures that the protective performance is reliable for the life of the case, safeguarding critical assets through countless trips and handling events. Its lightweight nature, a benefit of perforation, also helps keep overall shipping costs down, adding economic durability to its physical attributes.


 English
English
 Español
Español
 ++86-0512-66079229
++86-0512-66079229